What is the Eisenhower Matrix?
The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Eisenhower Decision Matrix, Eisenhower Box, and Urgent-Important Matrix, is a time and task management tool that helps individuals prioritize their tasks by considering two factors: urgency and importance.
It is named after Dwight D. Eisenhower, the 34th President of the U.S., who was known for his effective time management strategies.
To use the Eisenhower Matrix, first identify all the tasks you need to complete. Then, based on the urgency and importance of each one, place it in one of the four quadrants of the matrix:
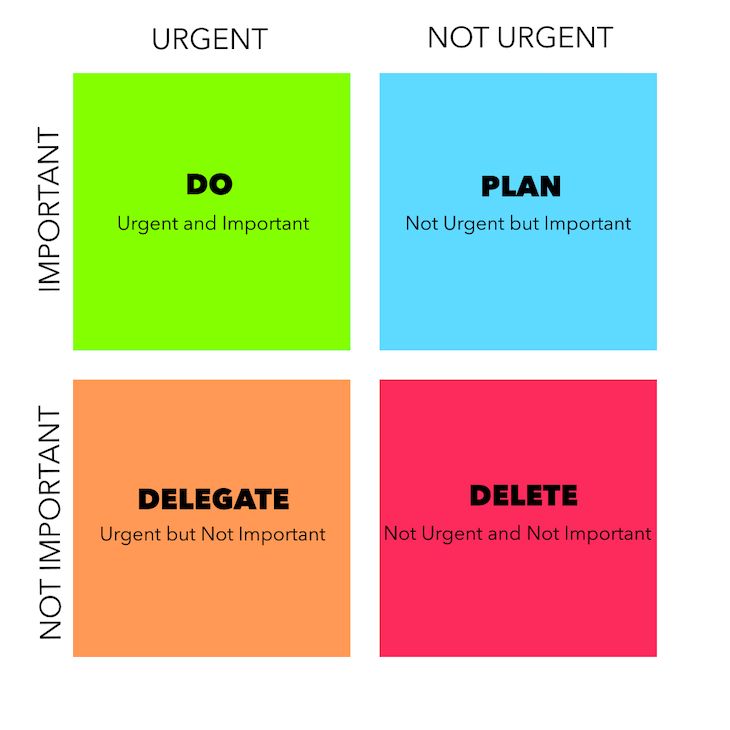
Here’s what each quadrant of the Eisenhower Matrix represents:
Urgent and important — Tasks that you need to complete as soon as possible. These are your top priority
Not urgent but important — Tasks that are critical but don’t have a pressing deadline. You should schedule time for them, otherwise, they might become urgent
Urgent but not important — Tasks that are pressing but not important. If possible, you should delegate them
Not urgent and not important — Tasks that are neither urgent nor important. You should eliminate them if possible
Who uses the Eisenhower Matrix?
Anyone who needs to manage their work can use this approach. It is particularly useful for project managers because it helps them focus on the most important tasks and avoid being overwhelmed by urgent but unimportant tasks.
If you’re a product manager or a project manager, you might use the Eisenhower Matrix to do things such as:
Identify and prioritize project tasks — Determine what tasks need to be completed for a and place them in the appropriate quadrant based on their level of urgency and importance. This will help you focus on the most important tasks first
Delegate tasks — Identify tasks that are urgent but not important and delegate them to team members or other resources if possible. This will free up your time to focus on more important tasks
Manage project resources — Identify tasks that are important but not urgent and schedule them in advance to ensure that they are completed on time. This will help you manage your resources effectively and avoid last-minute rushes to complete tasks
Monitor progress — Track your progress on tasks and identify any bottlenecks or roadblocks. This will help you stay on track and ensure that your project stays on schedule
By using the Eisenhower Matrix, you can effectively manage your time and resources and ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
Eisenhower Matrix example
Let’s see an example of how the Eisenhower Matrix works in practice.
In this example, the project manager has identified the following tasks:
- Write project proposal (quadrant 1)
- Develop project plan (quadrant 1)
- Conduct market research (quadrant 2)
- Attend team meeting (quadrant 3)
- Write a report on competitor analysis (quadrant 4)
Based on the level of urgency and importance of each task, the project manager has placed them in the appropriate quadrant of the matrix:

Eisenhower Matrix Example
Here’s how you can read the example Eisenhower Matrix above:
- The project manager should focus on the tasks in quadrant 1 first because they are both urgent and important
- The task in quadrant 2 also warrants attention because it is important but not urgent
- The task in quadrant 3 can be delegated or postponed because it is urgent but not important
- The task in quadrant 4 can be eliminated, as it is neither urgent nor important
How to categorize your tasks
Categorizing tasks using the Eisenhower Matrix can be a helpful way to prioritize your tasks and manage your time effectively. To realistically categorize your tasks, it is important to be honest with yourself about the level of importance and urgency of each task.
Before you begin categorizing your tasks, take some time to think about what is important to you and your goals. This will help you prioritize tasks that align with your values and objectives.
Think about the potential consequences of not completing a task. If the task is important, there will likely be negative consequences if it is not completed. On the other hand, if the task is not important, the consequences of not completing it may be minimal.
Establish deadlines for each task to help determine its level of urgency. A task with an imminent deadline is likely to be more urgent than a task with a longer timeline.
It is important to be consistent in your categorization of tasks. If you consistently categorize tasks based on their level of importance and urgency, you will be better able to prioritize your time and efforts.
From time to time, review and update your categorization of tasks, as priorities can change over time. Make sure to reassess the level of importance and urgency of your tasks regularly to ensure that you are focusing on the most important tasks.
How to get your team using the Eisenhower Matrix
If you plan to use the Eisenhower Matrix, you first need to explain the concept of the Eisenhower Matrix to your team and how it can be used to prioritize work and manage time efficiently.
Have each team member identify all the tasks they need to complete, including both work-related and personal tasks.
Then, have team members categorize their tasks using the matrix, placing each task in the appropriate quadrant based on its level of importance and urgency.
Encourage team members to focus on tasks in quadrant 1 first because they are both urgent and important. They should also give attention to tasks in quadrant 2, which are important but not urgent. Tasks in quadrant 3 can be delegated or postponed, while tasks in quadrant 4 should be eliminated if possible.
Encourage team members to regularly review and update their task priorities. This will help them stay on track and ensure that they are focusing on the most important tasks.
Limitations
Like any other framework or tool, the Eisenhower Matrix is not a one-size-fits-all solution and has some limitations.
For one, categorization of tasks into the quadrants of the matrix can be subjective because the level of importance and urgency of tasks can vary depending on the individual and the context. This can make it difficult to determine the appropriate categorization of certain tasks.

